The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is a regional economic forum established in 1989 to leverage the growing interdependence of the Asia-Pacific.
APEC’s 21 members aim to create greater prosperity for the people of the region by promoting balanced, inclusive, sustainable, innovative and secure growth and by accelerating regional economic integration.
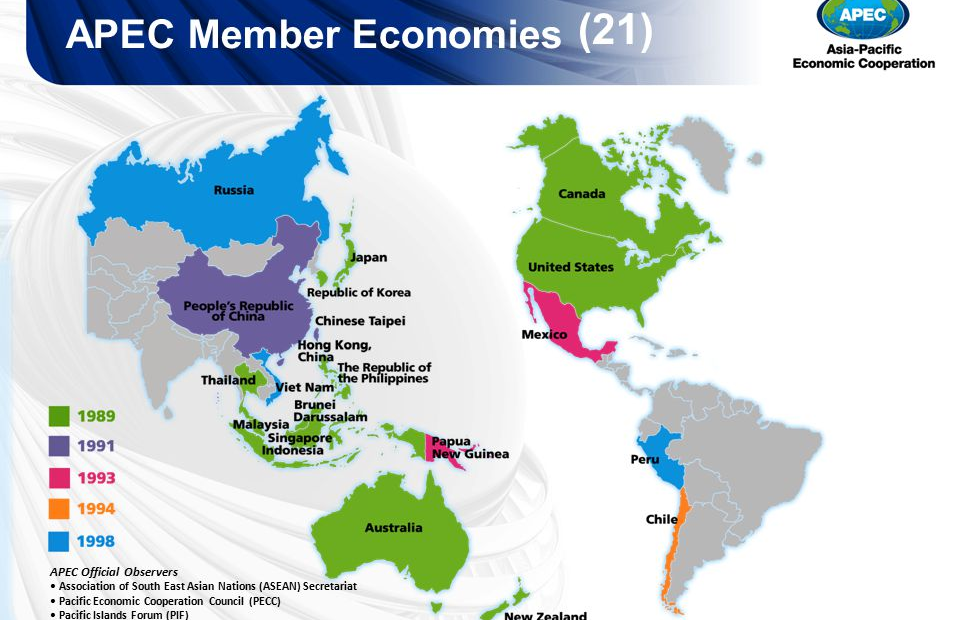
APEC’s 21 member economies are Australia; Brunei Darussalam; Canada; Chile; People’s Republic of China; Hong Kong, China; Indonesia; Japan; Republic of Korea; Malaysia; Mexico; New Zealand; Papua New Guinea; Peru; The Philippines; The Russian Federation; Singapore; Chinese Taipei; Thailand; United States of America; Viet Nam.
APEC’s 21 economies cover about 2.9 billion, or 38 percent of world population, with a combined gross domestic product (GDP) of US$52 trillion in 2020, accounting for 62 percent of world GDP and combined trade accounting for 48 percent of global trade in 2020, according to apec.org.
APEC ensures that goods, services, investment and people move easily across borders. Members facilitate this trade through faster customs procedures at borders; more favorable business climates behind the border; and aligning regulations and standards across the region. For example, APEC’s initiatives to synchronize regulatory systems is a key step to integrating the Asia-Pacific economy. A product can be more easily exported with just one set of common standards across all economies.
APEC: Cooperation and Consensus
APEC operates as a cooperative, multilateral economic and trade forum. Member economies participate on the basis of open dialogue and respect for views of all participants. In APEC, all economies have an equal say and decision-making is reached by consensus. There are no binding commitments or treaty obligations. Commitments are undertaken on a voluntary basis and capacity building projects help members implement APEC initiatives.
APEC Financial cooperation
The Bank of Thailand (BOT) and Finance Ministry have created mechanisms for digital domestic and international payments with a cross-border payment system using digital tools, like QR payment, according to the framework discussed at the APEC finance ministers’ meeting in October. Thailand is now working on cross-border QR payments with Cambodia, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, Singapore, and Vietnam. The PromptPay-PayNow connectivity between Thailand and Singapore already allows users to receive financial transactions via mobile phones, according to the BOT.
Thailand’s policy priorities for APEC 2022:
OPEN, CONNECT and BALANCE
Thailand’s theme for APEC 2022 is to make APEC OPEN to all opportunities, CONNECT in all dimensions, and BALANCE in all aspects.
Open to all Opportunities
To revitalize recovery, APEC must leverage its traditional strengths by facilitating open trade and investment, improving the business environment, and advancing regional economic integration, leveraging digitalization and innovation while continuing to support a rules-based multilateral trading system with the World Trade Organization at its core.
Connect in all Dimensions
Two years into the pandemic, disrupted connectivity remains one of the pressing unresolved issues in the region. To revive growth, APEC 2022 will focus on restoring connectivity by resuming safe and seamless cross-border travel, reinvigorating tourism and the services sector, facilitating business mobility as well as increasing investment in health security.
Balance in all Aspects
The past two years have unbalanced the region, worsening inherent inequalities that make economies vulnerable to shocks while highlighting current environmental challenges. To address this, APEC must integrate inclusivity and sustainability objectives in tandem with economic goals.
Discover more from Thailand Business News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.















You must be logged in to post a comment.